What is DGPS? Functioning, Limitations & Features
Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) is an enhancement to Global Positioning System that uses a network of fixed, ground-based reference stations to broadcast the difference between the positions indicated by the satellite systems and the known fixed positions. These stations broadcast the difference between the measured satellite pseudo ranges and actual (internally computed) pseudo ranges, and receiver stations may correct their pseudo ranges by the same amount. The correction signal is typically broadcast over UHF radio modem.
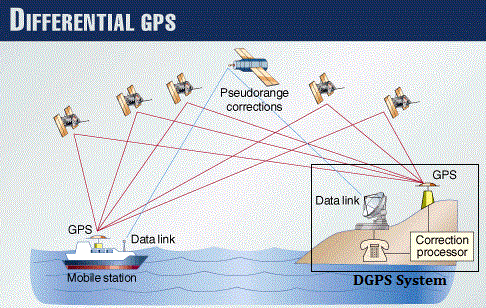
DGPS techniques are called the Ground Based Augmentation System and Ground based Regional Augmentation Systems. Both of these systems broadcast corrections via the aviation VHF band.
A similar system that transmits range corrections from orbiting satellites instead of ground-based transmitters is called a Satellite Based Augmentation System.
Features of DGPS (Differential Global Positioning System)?
- To overcome the disadvantages of accuracy denial.
- Systems are totally automatic.
- Improve the accuracy of the GPS fix only in areas where the system operates, typically about 200 nm.
- Additional equipment must be installed.
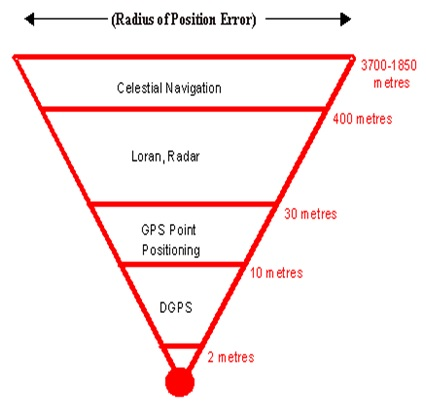
- position updates of 0.5 seconds reported position-fix accuracy of about 1 to 3 metres rms
- Still dependent upon the supplier of the GPS signals.
Differential GPS (DGPS) is a system in which differences between observed and
computed co-ordinates ranges (known as differential corrections) at a particular
known point are transmitted to users (GPS receivers at other points) to upgrade the
accuracy of the users receivers position.
Differential Correction :
Differential correction is a technique that greatly increases the accuracy of the collected DGPS data. It involves using a receiver at a known location – the “base station“ and comparing that data with DGPS positions collected from unknown locations with “roving receivers.”
Limitation & Errors of DGPS:
a) International Limitation of Accuracy
b) Receiver Independent Exchange Format
c) Reference System Co-ordinates
Methods used to Transmit Corrections:
- Computing & transmitting – a position correction in terms of Lat, Long & altitude i.e. x, y, z co-ordinates.
- Computation of pseudo range correction to each satellite which is then broadcasted to the user and applied to the user‟s pseudo range measurement before the position is calculated by the onboard receiver resulting in a higher accuracy of position fix.
- DGPS removes common-mode errors, those errors common to both the reference and remove receivers (not multipath or receiver noise). Errors are more often common when receivers are close together (less than 100 km). Differential position accuracies of 1-10 meters are possible with DGPS based on C/A code SPS Signal.
DGPS calculate even more accurate position than the GPS?
- DGPS enhances the accuracy of a GPS receiver. Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) is an enhancement to Global Positioning System that provides improved location accuracy, from the 15-meter nominal GPS accuracy to about 10 cm in case of the best implementations.
- DGPS uses a network of fixed ground-based reference stations to broadcast the difference between the positions indicated by the GPS satellite systems and the known fixed positions.
- These stations broadcast the difference between the measured satellite pseudo ranges and actual (internally computed) pseudo ranges, and receiver stations may correct their pseudo ranges by the same amount.
- The digital correction signal is typically broadcast locally over ground-based transmitters of shorter range.